Definition of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition in which the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as two numbers - systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. A normal blood pressure reading is 120/80 mmHg or lower, while a high blood pressure reading is 130/80 mmHg or higher.
Explanation of the Silent Killer
High blood pressure is often referred to as the silent killer because it often has no noticeable symptoms. Many people may have high blood pressure for years without realizing it, which can lead to damage to the body's organs and systems. High blood pressure is a serious condition that can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other health problems. It is essential to understand how high blood pressure affects health, the risk factors, and the prevention and management of the condition.
Importance of understanding how high blood pressure affects health
Understanding how high blood pressure affects health is crucial because it is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a leading cause of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems, which can be life-threatening. High blood pressure is a manageable condition, and with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to control and reduce the risk of complications. Therefore, it is essential to know the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for high blood pressure to prevent long-term damage to the body and maintain good health.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
Primary Hypertension
Primary hypertension, also known as essential hypertension, is the most common type of high blood pressure. The exact cause of primary hypertension is unknown, but it is believed to develop over time due to a combination of factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Secondary Hypertension
Secondary hypertension is a less common type of high blood pressure that occurs due to an underlying medical condition or medication. Medical conditions that can cause secondary hypertension include kidney disease, hormonal disorders, and sleep apnea. Certain medications such as birth control pills, decongestants, and steroids can also cause secondary hypertension.
Risk Factors
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing high blood pressure. These include age, family history of high blood pressure, obesity, physical inactivity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, stress, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and sleep apnea. It is important to be aware of these risk factors to take steps to reduce the risk of developing high blood pressure.
Effects of High Blood Pressure on the Body
Cardiovascular System
High blood pressure can have a significant impact on the cardiovascular system. It can cause damage to the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, a condition where the arteries become narrow and hardened, which can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. High blood pressure can also cause the heart to work harder to pump blood, leading to enlargement and damage to the heart muscle.
Nervous System
High blood pressure can affect the nervous system by damaging the blood vessels and nerves that supply the brain. This can increase the risk of stroke, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), and other neurological problems. High blood pressure can also cause headaches, dizziness, and problems with vision.
Kidneys
High blood pressure can damage the kidneys by causing damage to the blood vessels that supply the kidneys, leading to reduced blood flow and kidney function. This can result in chronic kidney disease or kidney failure, which can be life-threatening.
Eyes
High blood pressure can also affect the eyes by causing damage to the blood vessels that supply the retina, leading to retinopathy, a condition where the retina becomes damaged and can result in vision loss.
Other Organs and Systems
High blood pressure can also affect other organs and systems in the body, including the lungs, bones, and sexual organs. It can increase the risk of pulmonary embolism, osteoporosis, and sexual dysfunction.
It is crucial to manage high blood pressure to prevent long-term damage to the body's organs and systems.
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
Symptoms of Acute Hypertensive Crisis
An acute hypertensive crisis is a severe form of high blood pressure that requires immediate medical attention. The symptoms of an acute hypertensive crisis include severe headache, chest pain, shortness of breath, severe anxiety, confusion, vision changes, and seizures. If left untreated, an acute hypertensive crisis can lead to a stroke or heart attack.
Symptoms of Chronic High Blood Pressure
Chronic high blood pressure is a long-term condition that often has no noticeable symptoms, which is why it is often called the "silent killer." However, some people with chronic high blood pressure may experience symptoms such as headache, dizziness, blurred vision, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue. These symptoms can be a sign of an underlying medical condition and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
It is important to have regular blood pressure checks to monitor blood pressure levels, even if there are no noticeable symptoms. Early detection and management of high blood pressure can prevent complications and improve overall health.
Diagnosis and Treatment of High Blood Pressure
Diagnosis
High blood pressure is diagnosed by measuring blood pressure using a blood pressure cuff. A healthcare provider may perform multiple readings to confirm a diagnosis of high blood pressure. They may also order additional tests to check for underlying medical conditions that may be causing high blood pressure.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes are often the first line of treatment for high blood pressure. These changes include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, reducing salt intake, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress. These lifestyle changes can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications.
Medications
If lifestyle changes are not enough to control high blood pressure, medications may be prescribed. There are several types of medications available to treat high blood pressure, including diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers. The choice of medication will depend on the individual's medical history and blood pressure level.
Surgery
In rare cases, surgery may be required to treat high blood pressure. This may include procedures to remove blockages in the arteries, repair damaged blood vessels, or remove a damaged kidney. These procedures are typically reserved for cases of severe high blood pressure that are not responding to other forms of treatment.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the individual's needs and medical history. Regular monitoring and management of high blood pressure can prevent complications and improve overall health.
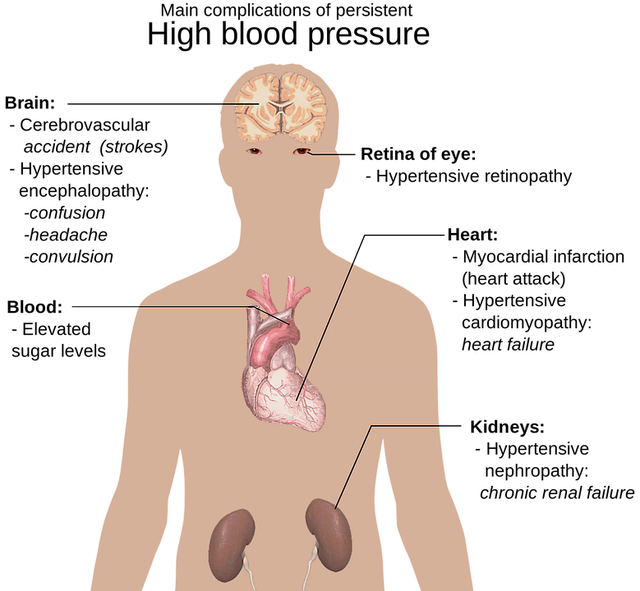
Complications of High Blood Pressure
Cardiovascular Complications
High blood pressure can lead to a range of cardiovascular complications, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, stroke, heart failure, and peripheral artery disease. These complications can be life-threatening and can significantly impact an individual's quality of life.
Kidney Complications
High blood pressure can cause damage to the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to reduced kidney function, chronic kidney disease, and kidney failure. These complications can require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Eye Complications
High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to retinopathy, a condition that can cause vision loss. In severe cases, high blood pressure can cause a retinal detachment, which can lead to permanent vision loss.
Other Complications
High blood pressure can also increase the risk of other complications, including aneurysm, cognitive decline, sexual dysfunction, bone loss, and sleep apnea.
It is important to manage high blood pressure to prevent these complications from occurring. Early detection and management of high blood pressure can improve overall health and quality of life.
Prevention of High Blood Pressure
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can help prevent high blood pressure. These include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, reducing salt intake, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress. These lifestyle modifications can also help lower blood pressure in individuals with prehypertension.
Regular Check-ups
Regular blood pressure checks are important for early detection and management of high blood pressure. Blood pressure should be checked at least once a year, or more frequently if there is a history of high blood pressure or other risk factors.
Risk Reduction
Reducing other risk factors can also help prevent high blood pressure. These include managing diabetes, reducing cholesterol levels, and treating sleep apnea. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce the risk of developing high blood pressure.
In conclusion, high blood pressure is a serious condition that can lead to a range of complications. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and complications of high blood pressure, as well as the prevention and treatment options available. Making lifestyle modifications, having regular check-ups, and reducing other risk factors can help prevent high blood pressure and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Recap of the effects of high blood pressure on health
High blood pressure is a serious condition that can cause a range of health complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, eye damage, and more. It is often called the "silent killer" because it may not have any noticeable symptoms until it has already caused significant damage to the body.
Importance of prevention and management of high blood pressure
Preventing and managing high blood pressure is essential for maintaining good health and preventing serious complications. Lifestyle modifications, regular check-ups, and medication can help manage high blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications.
Final thoughts
Understanding the effects of high blood pressure on health, as well as prevention and treatment options, is crucial for maintaining good health. By taking steps to prevent and manage high blood pressure, individuals can improve their overall health and reduce their risk of serious health complications. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to individual needs and medical history.